Dapeng Town Industrial Park, Tongshan District, Xuzhou City, Jiangsu Province, China
The advantages of tubular truss nodes are primarily achieved through the following node configurations:
Intersecting Nodes: This is the most classic and common form. The ends of the branch pipes are cut according to a three-dimensional mathematical model into complex curved shapes that perfectly match the outer surface of the main pipe, then directly welded. This is key to achieving “smooth force flow transmission.”
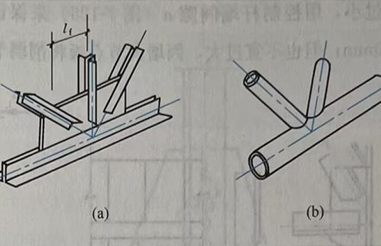
(a)Angle steel node
(b)Tube Truss Node
For a more intuitive comparison, we can contrast this with traditional angle steel truss joints:
| Characteristics | Tube Truss Node | Angle steel node |
| Mechanical Properties | better | good |
| Aesthetic appeal | best | good |
| Economy | Overall cost-effectiveness, saving steel materials, but with high node costs. | The node fabrication is straightforward, but it requires a large amount of steel. |
| Applicable span | Large-span (airports, theaters, stadiums) | Medium-to-small span (standard industrial buildings) |
| Construction | Highly demanding factory prefabrication and welding processes, yet simple on-site installation. | Node installation is straightforward, but on-site installation requires significant construction effort. |
In summary, the advantage of tubular truss nodes lies in their ingenious integration of structural efficiency, architectural aesthetics, and cost-effectiveness. By employing advanced manufacturing techniques—such as BIM-based 3D intersecting line cutting and automated welding—they resolve complex stress distribution challenges, making them one of the preferred solutions for modern large-span spatial structures.